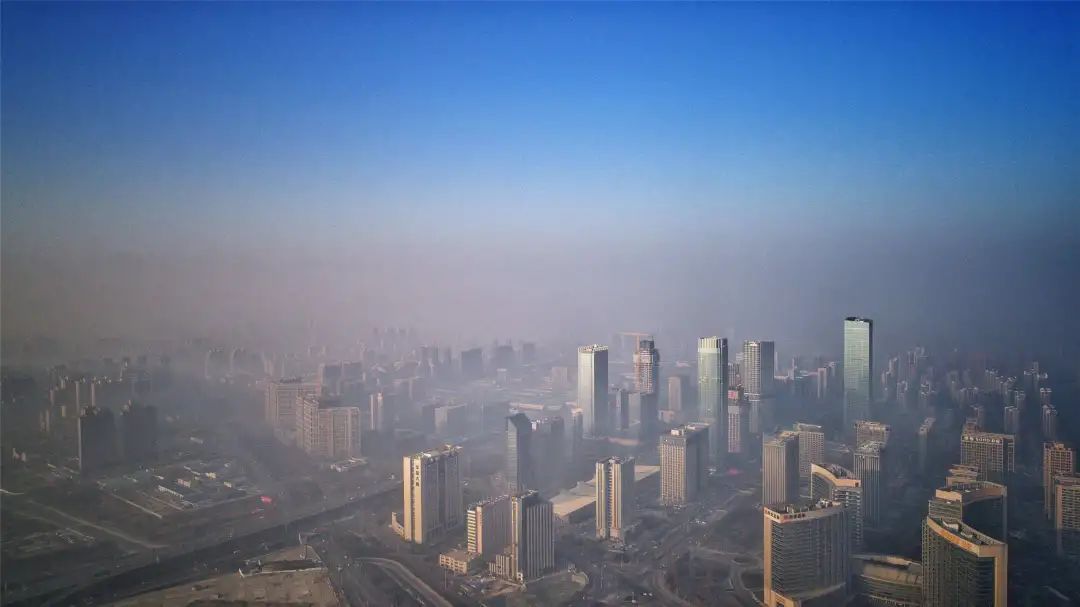
The dust detector is mainly used to measure the atmospheric environment and is suitable for various environmental research institutions, meteorology, public health, environmental monitoring, and air pollution research. It is applied in various environments such as disease control centers, mines, metallurgy, power plants, chemical manufacturing, health supervision, environmental protection, and online environmental monitoring.

And particle counters are applied in clean rooms, such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, precision machinery, semiconductors, biotechnology and other industries, to monitor the purification effect and cleanliness level of various clean levels of workbenches, clean rooms, and clean workshops, in order to ensure the production quality of products.
So besides the different application scenarios, what are the specific differences between dust detectors and dust particle counters?
Firstly, let's introduce the term 'aerosol', which I believe everyone is familiar with in recent years due to the pandemic. It refers to a gaseous dispersion system composed of solid or liquid particles suspended in a gas medium. The density of these solid or liquid particles can differ slightly or significantly from the density of the gas medium.
The size of aerosol particles is usually between 0.01 and 10 μ m, but due to their wide range of sources and formation reasons, for example, the particle size of plant aerosols such as pollen is between 5-100 µ m, and the particle size of aerosols produced by the combustion of wood and tobacco is usually between 0.01-1000 µ m. Therefore, the shapes of particles are diverse, ranging from almost spherical, such as liquid droplets, to sheet, needle, and other irregular shapes. From the perspective of fluid mechanics, aerosols are essentially multiphase fluids with gas as the continuous phase and solid and liquid as the dispersed phase.
Clouds, fog, dust in the sky, smoke formed from unburned fuel in boilers and various engines used in industry and transportation, solid dust formed during mining, quarrying and stone processing, and grain processing, as well as artificial smoke screens and toxic smoke, are all specific examples of aerosols. The PM2.5 and PM10 we refer to in our daily lives are solid particulate matter in atmospheric aerosols. So the dust detector can also be called an aerosol detector.
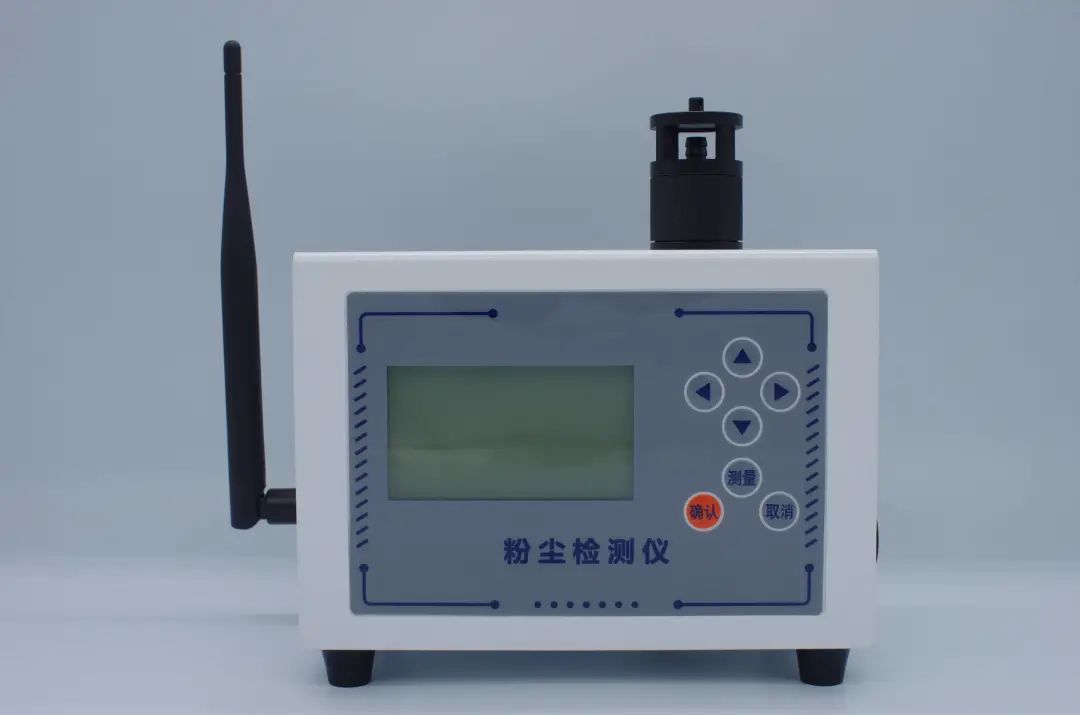

Dust detector
The dust detector inhales the aerosol to be tested into the detection chamber through a sampling pump, and divides the aerosol into two parts at the branching point. One part is filtered into clean air after passing through an efficient filter, which serves as a protective sheath to protect the components in the sensor room from contamination by the gas to be tested.
The other part of the aerosol is directly introduced into the sensor chamber as the sample to be tested. In the sensor room, the main components are laser diodes, lens groups, and photodetectors. During the detection process, a laser diode first emits laser light, which forms a thin layer surface light source through a lens group. When thin layer light is irradiated on the aerosol flowing through the sensor chamber, scattering occurs, and the scattered light intensity is detected by a photodetector.
The electric detector generates an electrical signal after being illuminated, which is proportional to the mass concentration of the aerosol. Then multiply by the voltage calibration coefficient, which is obtained by measuring specific concentrations of aerosols.

Dust particle counter
Principle of dust particle counter: The particle counter extracts sampling gas through a sampling pump. In the laser chamber, the sampling gas is irradiated with laser, and the frequency of the flash reflected by the particles represents the number of particles, while the reflected light intensity represents the particle size.
Due to the lack of sheath gas protection for the components in the laser room, the laser particle counter should be used in a clean environment to prevent damage to the laser sensor.
When there are loose particle materials, dust sources, and spray at the measuring place, it must be kept at least 12 inches away from the inlet and outlet pipes to prevent particles and liquids from polluting the sensors and pipelines.
In summary, the laser dust analyzer not only adopts the sheath gas protection function of the clean air path, but also has a more complex internal detection sensor structure, effectively protecting the components and preventing them from being damaged by pollutants. Therefore, it can be used for a long time in relatively complex and heavily polluted environments.
However, due to the lack of sheath gas in the gas path design and the relatively simple structure of the detection sensor, the dust particle counter can only be classified according to a few effective particle sizes, resulting in significant errors when converted to dust concentration (estimating 8-channel classification with a calculation error greater than 30%; 2-channel classification with a calculation error greater than 50%). Therefore, particle counting measurements can only be carried out in relatively clean spaces.
Do you now know the difference between particle counters and dust detectors through the above introduction?

The particle counter product series developed and produced by SuXin Environment covers flow rates ranging from 2.83L/min to 100L/min. It has features such as handheld, desktop, and online monitoring functions, which can basically meet the current needs of various industries for such products.



